Basic Dimensions and Design Requirements of Seats
 May 19,2025
May 19,2025
 Topmax Furniture
Topmax Furniture
The design of seating furniture must strictly refer to human body measurement data to determine the optimal size. At the same time, the pressure on the front edge and legs of the chair should be minimized. The design of the chair back and cushion should also fully consider reducing the burden on the human body and making people sit comfortably. Different daily life behaviors require the use of seats with different functions, and the requirements for the comfort of seats are also different. According to the different uses of seats, Chair Supplier generally divides them into the following three categories.

Work seats
Work seats are mainly used for people's daily work, meetings, and learning activities. They are mostly used in places such as office spaces or cultural spaces. The main product types include stools, backrest chairs, armchairs, etc. The characteristics of this type of seats are that they can not only meet people's work and study needs, but also provide proper rest for the body, making people feel convenient and comfortable while improving work efficiency.
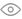
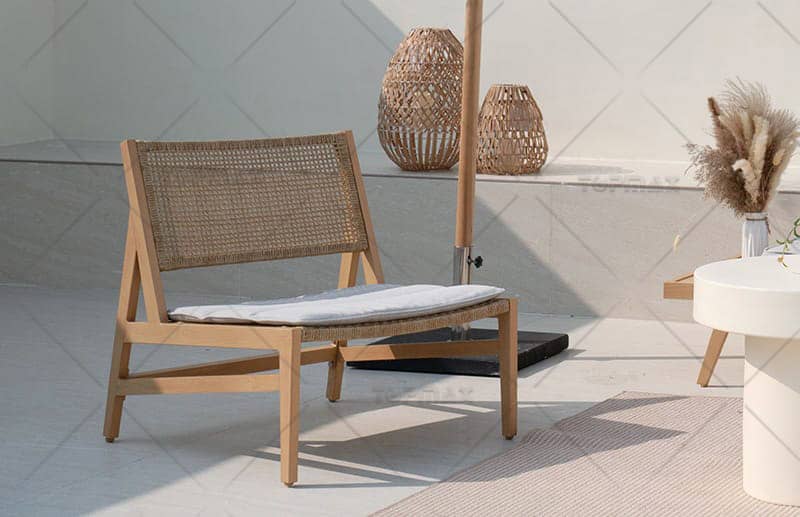
1. Seat height: Seat height refers to the vertical distance between the seat surface of the seat and the ground. However, since the seat surface of the chair is often tilted backward or sometimes made into a concave surface, we usually use the vertical height from the front edge of the seat surface to the ground as the seat height of the chair. The seat height is one of the most important factors affecting the comfort of sitting posture. An unreasonable seat height will lead to a bad sitting posture, and sitting for a long time will cause fatigue in the waist and back. By measuring the lumbar spine mobility of people sitting on stools of different heights, it can be seen that when the seat height is 400mm, the lumbar spine mobility is the highest, that is, it is most likely to feel fatigue; when the seat height is slightly higher or lower than 400mm, the lumbar spine mobility of the human body will decrease, and the comfort will increase accordingly.
Different Sitting Heights and Lumbar Mobility
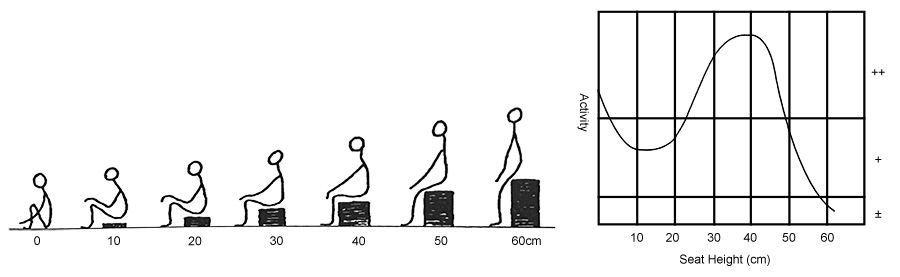
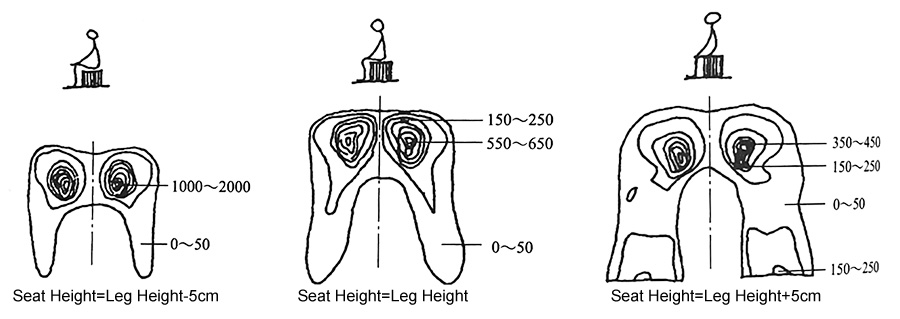
Chair Supplier believes that although the backrest of the seat can relieve some fatigue, its seat height should not be too low or too high, because it is closely related to the distribution of body pressure on the seat surface. As shown in the figure below, there are significant differences in the distribution of body pressure under different sitting heights: when the seat surface is too low, the front of the thigh cannot touch the seat surface, and the body pressure distribution is too concentrated, which makes people feel pain easily, and also makes people bend forward, increase the load on the back muscles, and cause the center of gravity of the human body to be too low, making it difficult to stand up; when the seat surface is too high, the feet cannot touch the ground, so that the soft tissue near the knee of the front half of the thigh is compressed, which will lead to poor blood circulation and swelling and numbness of the tendon; only when the seat surface height is equal to the lower leg height, the pressure is small and the most comfortable. Therefore, when designing, we should seek a reasonable seat height and body pressure distribution. In actual design, the seat height should be less than the vertical distance from the user's knee to the ground, so that the calf has a certain room for movement.
Different Sitting Heights and Body Pressure Distribution
2. Seat width: According to the sitting posture and movement of the human body, the width of the seat surface is generally wide in front and narrow in the back. The front edge width is the front width of the seat, and the back edge width is the back width of the seat. The width of the seat surface should allow the buttocks to be fully supported and have appropriate room for movement, which is convenient for adjusting the sitting posture of the human body. If it is a row of seats, the seat width should be slightly larger than the distance between the two elbows of a person to ensure free movement of the person. During the manufacturing process, Chair Supplier generally uses a backrest chair with a seat width of no less than 380mm to meet the functional needs. The seat width should not be too wide, and should be based on the comfortable shoulder width of a naturally hanging arm.
Examples of Uncomfortable Seat Height
3. Seat depth: refers to the distance from the front edge to the back edge of the seat surface, which has a great impact on the comfort of the human body's sitting posture. If it is too deep, the waist support point will be suspended, the knee pit will be compressed, causing numbness and fatigue, and it will be difficult to get up. The appropriate seat depth is usually less than the horizontal length of the thigh when sitting, so that the front edge of the seat is about 60mm away from the calf to ensure the freedom of movement of the calf. During manufacturing, Chair Supplier will select a seat depth of 380~420mm based on the average horizontal length of the thigh of the Chinese body when sitting. In normal work, the lumbar spine and pelvis are close to a vertical state, so for ordinary work chairs, the seat depth can be slightly shallower.
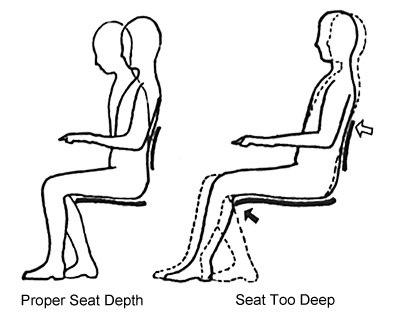
Body and Sitting Depth
4. Seat surface curvature: When the human body is in a sitting position, the curvature of the seat surface will also affect the distribution of body pressure, thus causing changes in the feeling when sitting. As shown in the figure below, the body pressure distribution on the left is better, while the right is not so good. This is because the pressure on the left is mostly concentrated on the ischial support point, while the right side has a considerable pressure to be borne by the soft tissue of the legs. Therefore, Chair Supplier recommends that the seat surface should be made of semi-soft and slightly hard materials, and the seat surface can also be slightly curved or flat in front and back, so as to reduce the pressure area of the buttocks muscles, increase the comfort of the seat and facilitate the human body to sit up.
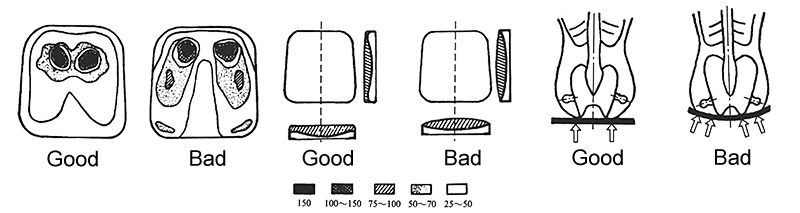
Seat Curvature and Body Pressure
5. Seat surface inclination: The seat surface design of the general seat is tilted backward at an angle of 3°~5°, which is conducive to the rest and relaxation of the human body. However, when people are working, the spine and pelvis are close to a vertical state, or even leaning forward. Therefore, for work chairs, a horizontal seat surface is more reasonable than a backward seat surface, and sometimes a forward seat surface design can also be considered. As shown in the figure below, the W Chair designed and developed by the German design team W team has a slightly forward-leaning seat surface and a design that supports the calves on the left and right sides. This allows people to naturally lean forward when working, which is more conducive to concentration and improved work efficiency.

6. Chair backrest: The chair backrest can support the human body, relax the muscles of the waist and back, and relieve fatigue. There are three key support points in the height of the backrest: shoulder support, waist support, and neck support. The shoulder support should be lower than the shoulder blade, about 460mm high, and the inner angle of the shoulder blade should not touch the chair back. The waist support should be lower than the upper edge of the lumbar spine, and the support point should be located in the upper waist concave, with a height of 180~250mm. The neck support should be higher than the cervical spine point, generally not less than 660mm. The width of the chair backrest is generally 350~480mm, and the comfort will also increase with the increase of width. Because the body leans forward when working, general work chairs only have waist support to facilitate free movement of the waist joint and upper limbs.
Resting seats
Resting seats are mainly used for people's daily rest and leisure. The most common product types are sofas, leisure chairs, reclining chairs, rocking chairs, etc. Compared with work seats, resting seats can relieve physical fatigue, make people relax to the maximum extent and get excellent comfort, thereby improving people's quality of life.

1. Seat height and width: The height of the front edge of the resting seat should be slightly less than the vertical distance from the popliteal fossa to the heel, about 330~380mm (excluding the elastic margin of the material). If thicker soft materials are used, the limit of elastic sinking should be used as the size criterion. The width of the seat surface is generally above 430~450mm.
2. Seat depth: Since most resting seats are padded, the seat surface and backrest will sink to a certain extent when sitting down, so the seat depth can be appropriately increased. The depth of a light sofa is between 480 and 500 mm; the depth of a medium-sized sofa is between 500 and 530 mm; the depth of a large sofa depends on the indoor environment, but it should not be too deep.
3. Sitting inclination angle and chair angle: The key to the design of a resting chair is the reclining angle of the seat surface and the angle between the seat surface and the backrest. The resting chair uses the inclination of the seat surface to allow the human body to shift its weight backward to the lower half of the backrest and the ischial tuberosity of the buttocks. With the change of different postures of the human body, the reclining angle of the seat surface and its angle with the backrest have a certain correlation. The larger the backrest angle, the larger the reclining angle of the seat surface. Generally, the larger the inclination angle, the stronger the rest and comfort. However, within a certain range, sometimes the inclination angle is too large, which is not conducive to people getting up, but causes trouble.
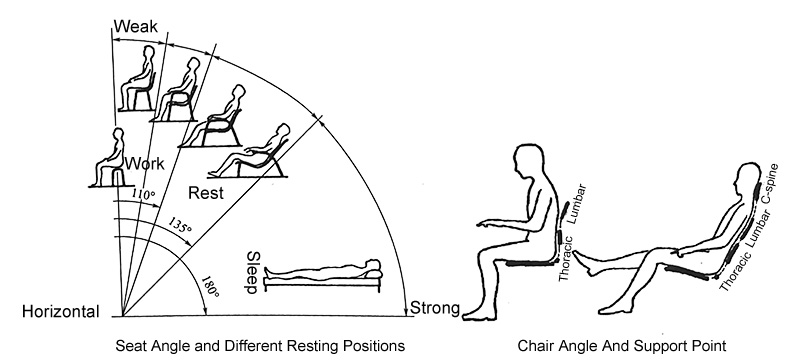
Generally, the inclination angle of sofa seats is 4°~7°, and the backrest angle is 106°~112°; the inclination angle of reclining chairs is between 6°~15°, and the backrest angle is 112°~120°. It is worth noting that as the angle between the seat and the backrest increases, the support points of the backrest must also increase.
4. Cushion material and elasticity: Resting seats generally use cushions to improve comfort, and the combination of cushion materials and elasticity is the key to comfort. Elasticity refers to the hardness of the material when people sit on it or the return degree of the material when people sit on it. Generally, the seat surface of a small sofa should sink about 70mm, and the seat surface of a large sofa should sink 80~120mm. If the seat surface is too soft and sinks too much, the angle between the seat surface and the backrest will become smaller, the abdomen of the person will be compressed, and it will be inconvenient to stand up.

For resting seats with backrests, the backrest should be softer than the seat surface, which is more conducive to the distribution of body pressure and convenient use. The lumbar part of the backrest should be slightly harder, and the elastic compression should be less than 35mm, while the elastic compression of the back should be between 30 and 45mm. When designing, the stable posture of the elastic body after sinking should be used as the basis for calculating the size of the furniture.
5. Armrest height and inner width: The setting of armrests can reduce the fatigue of the shoulders, back and upper limb muscles, and obtain a more comfortable rest effect. However, the height of the armrest must be appropriate. If it is too high or too low, the shoulders cannot sag naturally and are prone to fatigue. According to the distance between the elbow of the human body's naturally bent arm and the seat surface, the actual height of the armrest should be set at 200~250mm (the sinking of the seat surface should be subtracted during design). The net width of the armrest spacing should be slightly larger than the shoulder width of the human body, generally not less than 460mm, and 520~560mm is appropriate. Too wide or too narrow will increase the activity of the shoulder muscles and produce shoulder fatigue.
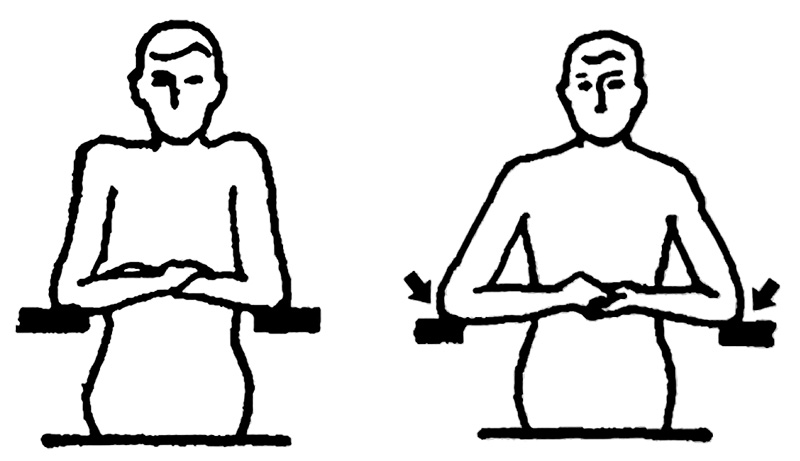
Example of Improper Handrail Spacing
The armrests can be slightly tilted as the angle between the seat and the backrest changes, with an angle of 10°~20°, which helps to improve the comfort of the seat. In terms of material selection, it is not advisable to choose materials that are too soft or have strong thermal conductivity, and the appearance of edges and corners should be avoided as much as possible.
Multifunctional seats
This type of seat is characterized by diversified functions and forms. On the basis of traditional furniture functions, it combines new materials and integrates new technologies to enrich the functions of modern seat furniture. As shown in the figure below, this seat was designed by Japanese designer Takafumi Honma, who used the combination of traditional wooden tenon structure and modern hardware to design this three-section "Rubik's Cube Chair". This seat has an adjustable structure, and the backrest can be raised and lowered according to different needs. The first section is a square stool for storage, the second section is a seat with a backrest, and the third section is a guardrail to protect the safety of children. It can not only meet the various needs of modern people, but also save space.
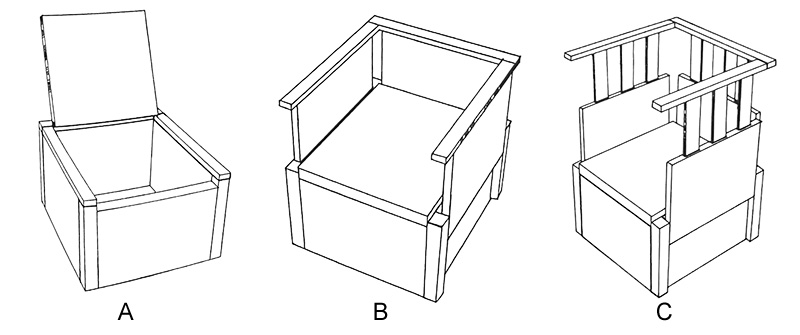
Rubik's Cube Chair
When designing multifunctional seats, we should pay attention to the variability of their form and the diversity of their functions, so that the seats can adapt to different environmental conditions, human postures, and user groups. At the same time, new materials and new technologies should be used to not only obtain new structural shapes, but also realize new functions of the seats.
 Inquire Now
Inquire Now


 Home
Home Development Trends and Directions of Chinese Furniture Industry
Development Trends and Directions of Chinese Furniture Industry  You May Also Like
You May Also Like 





















 Tel
Tel  Email
Email  ADDRESS
ADDRESS 














