What are the Materials Commonly Used in Furniture Manufacturing?
 May 16,2025
May 16,2025
 Topmax Furniture
Topmax Furniture
In the field of furniture manufacturing and design, furniture materials refer to the general term for various materials related to furniture, which are used for the production of furniture main structure, furniture surface decoration, local bonding and parts fastening. Materials are the material basis of furniture shape and structure, and are the premise and guarantee for the realization of furniture shape. Different materials give people different textures and aesthetic tastes due to their different physical and chemical properties. The main materials for Chinese furniture manufacturing can be mainly divided into natural materials such as natural wood, wood-based panels, bamboo, and wood, and artificial materials such as metal, plastic, and glass.
With the continuous emergence and development of new materials, new technologies and new processes, furniture materials are more often designed with two or more materials, so as to highlight the different styles and aesthetic characteristics of furniture, make the products rich and varied, and meet people's requirements for different shapes, structures and comfort. Kaare Kint, a famous Danish furniture designer, pointed out: "To maximize the properties of materials is the first principle of any perfect design."

Natural wood
Wood is a natural material with fine texture, beautiful texture, and easy processing and molding. It is also the longest-used and most used furniture material. There are many types of wood, which can generally be divided into two categories: coniferous wood (soft wood) and broadleaved wood (hard wood).
| Types | Material Characteristics | Typical Representatives |
| Softwood | The trunk is straight and tall, with straight texture, uniform material, light and soft wood, easy to process, high strength, small surface density and expansion deformation, and strong corrosion resistance. | Korean pine, larch, white pine, spruce, fir, Japanese cedar, hemlock, yew, fir, cypress, masson pine, Chinese pine, Yunnan pine, Douglas fir (Douglas fir), Chilean pine, etc. |
| Hardwood | The straight part of the trunk is generally shorter, the material is harder to process, the density is higher, the strength is high, the expansion and contraction, warping and deformation are large, and it is easy to crack, so it is suitable for making smaller furniture components. | Ash, elm, basswood, locust, poplar, maple, beech, jujube, sumac, yellow-barked locust, holly, alder, chestnut, holly, chestnut, Chinese holly, boxwood, rubber wood, nanmu, oak, teak, rosewood, camphor wood, rosewood, rosewood, wenge, ironwood, cherry wood, walnut wood, etc. |
Wood is not only a natural biological resource (Re-generation), but also a resource that can be reused (Reuse) and recycled (Recycle). It has the following advantages.
① Natural color and texture: Wood forms various coarse and fine straight and oblique textures due to different annual rings and wood grain directions. Through sawing, rotary cutting or planing, and splicing, it can be made into rich and beautiful patterns; at the same time, wood of different tree species also has different natural colors and lusters.
② Lightweight and high strength: Wood has high elasticity and toughness, can withstand large deformation without breaking, and is resistant to impact and vibration.
③ Easy to process: Wood can be used after being felled, sawn, dried, etc. It can be cut and decorated with simple tools or machinery, and can also be joined in a variety of ways such as tenons, glue, nails, screws, connectors, etc.
④ Low electrical conductivity: Since wood is a porous material, it has good insulation performance, slow heat conduction, and a small thermal expansion coefficient, which often gives people a sense of comfort and security in winter and coolness in summer. For example, in the design of urban public seats, metal materials often bring people all kinds of discomfort during use due to their high thermal conductivity. People feel too hot when sitting in summer, and feel cold in winter. In order to solve this problem, metal materials can be used in combination with wood, plastic materials and other materials in the design.
At the same time, wood also has disadvantages such as hygroscopicity (shrinkage and swelling), anisotropy, knots and insect eyes, susceptibility to insects, fungi and frogs, and flammability. Among them, the hygroscopicity of wood has a great influence on the processing and utilization of products. It will not only cause changes in the size, shape and strength of wood, but also cause deformation, cracking, warping and distortion of the board. After the wooden furniture is made, the shape and material will not change. At this time, the key factor that determines the intrinsic quality of the furniture is mainly the moisture content of the wood. In normal conditions, wood and its products will have a certain amount of moisture. In China, the percentage of the weight of water contained in wood to the weight of wood after absolute drying is defined as the moisture content of wood. Wood is a material with shrinkage and swelling properties. When the moisture content of wood is higher than the equilibrium moisture content of the environment, the wood will shrink by moisture removal, and vice versa, it will expand by moisture absorption. For example, the annual average equilibrium moisture content in Guangzhou is 15.1%, while that in Beijing is 11.4%. Wood dried to 11% is suitable for use in Beijing, but it will expand and deform when used in Guangzhou. Therefore, during the processing of furniture, the wood should be dried properly, and the moisture content of the material should be dried to below the equilibrium moisture content of the area of use, generally about 12% in the north, about 18% in the south, and about 16% in central China.
Wood-based panels
At present, although wood has many advantages, it still has defects such as easy deformation, cracking, and warping, and the utilization rate of products made from logs through various cutting processes is only 60%~70%, which is very wasteful. Wood-based panels are made of logs or processing residues through various processing methods. Wood materials. There are many types of wood materials. Currently, the commonly used wood materials in furniture manufacturing include plywood, particleboard, fiberboard, and blockboard. Wood-based panels have the advantages of large format, uniform texture, flat surface, easy processing, high utilization rate, small deformation, and high strength. The use of artificial panels to produce furniture has simple structure, novel shape, convenient production, and is easy to achieve standardization, serialization, generalization, and mechanization. Therefore, in the process of modern furniture manufacturing, artificial panels have gradually replaced the original natural wood and become an important raw material in wooden furniture. Except for a few square components that must be made of solid wood, most of the panel components are made of various artificial panels.
(1) Plywood
Plywood is made of logs that are peeled or sliced into veneers, and then glued with three or more odd-numbered veneers. The fiber directions of each veneer are perpendicular to each other. The top layer of the board is often made of veneer from high-quality tree species. The main tree species of plywood raw materials are camphor, eucalyptus, poplar, eucalyptus, etc., which have large and flat formats, are not easy to crack and warp. It is simple and easy to bend, and is suitable for furniture making and interior decoration. The specifications of plywood width (width x length) are mainly 915mmx1830mm, 915mmx2135mm, 1220mmx1830mm and 1220mmx2440mm. The thickness specifications are generally 2.6mm, 2.7mm, 3mm, 3.5mm, 4mm, 5mm, 5.5mm, 6mm, 7mm, 8mm, etc. (8mm and above are incremented by 1mm). (Added). Generally, three-layer plywood is 2.6-6mm, five-layer plywood is 5~12mm, seven-to-nine-layer plywood is 7-19mm, and eleven-layer plywood is 11~30mm.
In design, plywood can be used in conjunction with wood. It is suitable for large-format parts on furniture, such as door panels, panels, side panels, back panels, top panels, bottom panels of various cabinet furniture, bottom panels and panels of drawers, as well as molded parts such as back panels, seat panels, and sofa armrests of folding chairs. Polish female designer Alicja Prussakowska designed a shelf called "Mizu". Four pieces of plywood that can withstand a certain degree of bending are inserted in the middle of the product with iron wire. In this way, the overall shape of the shelf depends on the position and weight of the objects placed on it. Mizu means water in Japanese. The four wooden frames are like waves with ups and downs, which are highly decorative and reflect the personal taste of the user. Indian designer Karan Sngh Gandhi designed a chair based on the Mudra gesture (Mudra represents a polite gesture in Sanskrit. This gesture is very important in Indian culture, including yoga art, and symbolizes balance and meditation). The product is symmetrical on both sides, with both sides slightly raised to form a soft curve. A very thin white metal rod is used under the seat to simulate the appearance of two crossed hands.

(2) Particleboard
Particleboard is made of small-diameter wood, wood processing residues (board skin, cut ends, shavings, wood chips, sawdust, etc.), Logging residues and other plant materials are processed into fragments or shavings of certain specifications and shapes, which are dried, mixed with adhesives, hardeners, and waterproofing agents, and pressed at a certain temperature to form an artificial board, also known as particleboard. Particleboard has the advantages of relatively uniform structure, homogeneity in length and width, no growth defects, no need for drying, good processing performance, and high utilization rate. Therefore, it can be processed into large-format boards as needed. It is an ideal material for making furniture of different specifications and shapes. However, particleboard also has the characteristics of low surface tensile strength, large thickness expansion rate, easy edge shedding, not suitable for mortising, low nail holding force, poor cutting performance, large free formaldehyde release, and no surface Wood grain and other defects. The specifications of particleboard format (width x length) are mainly 915mmx1830mm, 915mmx2135mm, 1220mmx1830mm and 1220mmx2440mm. The thickness specifications are generally 4mm, 6mm, 8mm, 9mm, 10mm, 12mm, 14mm, 16mm, 19mm, 22mm, 25mm, 30mm, etc.
Particleboard is mainly used as a raw material for cabinet furniture in furniture manufacturing, such as skeleton load-bearing parts (side panels, top panels, horizontal grid panels, bottom panels, etc.), closures, decorations, functional parts (doors, drawers, etc.) and cabinet reinforcements (back panels, etc.) ). Because the edges are rough and easy to absorb moisture, the edges of furniture made of pattern board must be sealed with solid wood or plastic, and the surface must be pasted with veneer or other finishing materials before it can be used.

(3) Fiberboard
Fiberboard is made of wood or other plant fibers, and is made through chipping, pulping, molding, drying and hot pressing. It is often called density board. Fiberboard can be divided into high-density fiberboard (HDF, density is generally 0.8~0.9g/cm°), medium-density fiberboard (MDF, density is generally 0.4-0.8g/cm°), and soft fiberboard (LDF density is less than 0.4g/cm°) according to density. Medium-density fiberboard (MDF) and high-density fiberboard (HDF) have the advantages of large format, uniform structure, high strength, stable size, small deformation, and easy cutting (according to cutting, The board has the characteristics of strong edges, smooth surface, easy to directly glue various finishing materials, paint and print processing; while the soft fiberboard (LDF) has low density and relatively poor physical and mechanical properties.
The fiberboard format (width x length) specification is mainly 1220mmx2440mm. The thickness specifications are generally 6mm, 8mm, 9mm, 12mm, 15mm, 16mm, 18mm, 19mm, 21mm, 24mm, 25mm, etc.
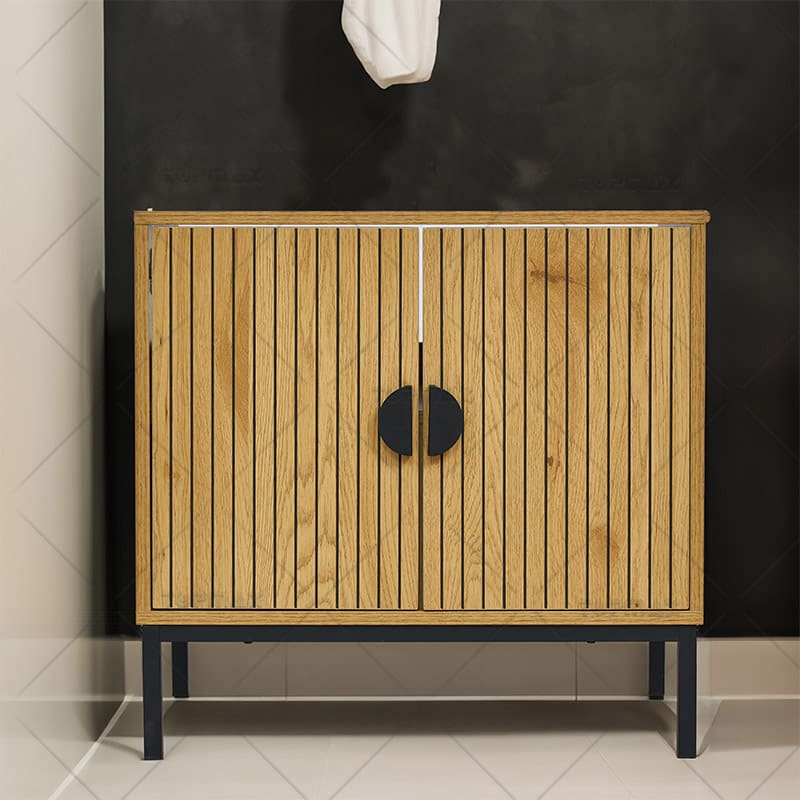

(4) Blockboard
Blockboard is commonly known as large core board. It is a solid core board made by arranging wood strips of the same thickness in parallel in the same direction, and gluing one or two layers of veneer on both sides according to the principle of symmetry, odd layers and perpendicular textures of adjacent layers. Therefore, blockboard is a solid core cladding material with solid wood. Plywood with a core is also called solid board. The structure of the blockboard is stable, not easy to deform, has good processing performance, high strength and nail holding power. It is a high-quality board that retains the original color of wood. It is widely used in furniture manufacturing and interior decoration, especially suitable for creating table panels and seat panels and structural load-bearing components.
The specifications of the blockboard format (width x length) are mainly 1220mmx1830mm, 1220mmx2440mm, etc. The thickness specifications are generally 12mm, 14mm, 16mm, 18mm, 19mm, 20mm, 22mm, 25mm, etc.
(5) Hollow board
The hollow board is a hollow composite structural board composed of a lightweight core material (hollow core board) and a cladding material. The hollow filler mainly includes square, grid, corrugated, etc. made of veneer strips, fiberboard strips, plywood strips, kraft paper, etc. Fillers in the form of corrugated, honeycomb, disc, etc. Hollow boards have the characteristics of light weight, small deformation, stable size, flat board surface and certain strength. In furniture manufacturing, the wooden frame and lightweight core material are usually glued on one or both sides with a composite board, hard fiberboard or decorative board and other covering materials to form a hollow board. The board specifications usually have no unified standard width and thickness and are produced by furniture manufacturers.
(6) Wood-plastic composite materials
Nowadays, as natural forest resources have been over-exploited by humans, the value of the remaining resources for maintaining ecological balance is far greater than processing and utilization, so various bio-based composite materials have begun to emerge. Among them, wood-plastic composite materials have developed rapidly and have become one of the new materials that many countries in the world give priority to promoting and applying, and are gradually replacing wood in furniture. Wood-plastic composite materials (Wo0d-Plastic Composites) is mainly based on natural plant fiber materials such as bamboo powder, rice husks, wheat straw, cotton stalks, etc., and is mixed with polyolefins such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS) and thermoplastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in a certain proportion, and extruded (or pressed) to make a reversible and recyclable multi-purpose green and environmentally friendly material. Because wood-plastic composites have the characteristics of both wood and plastic, they have excellent properties such as light weight, easy processing, high strength, low water absorption, insect resistance, corrosion resistance, and environmental protection. They are similar to the texture of wood in terms of vision and touch, giving people a warm and comfortable natural feeling. With the continuous improvement of production technology, the types of furniture made from it are increasing and the scope of use is becoming wider and wider. The products mainly include leisure tables and chairs, furniture structural components, etc.
Usually, in the wood-plastic composite material In products, mechanical connectors such as screws, bolts and rivets are often used to assemble thousands of parts, components and accessories in a certain structural form. Compared with screws and rivets, bolt connections have the advantages of sufficient tightness and toughness, convenient manufacturing and construction, large bearing capacity, high fatigue strength under repeated loads, safety and reliability, and beautiful appearance. They are often used to connect the main load-bearing components of the product. However, at this stage, due to the relatively small amount of research on this material, the setting of various parameters in the design is mostly determined by referring to the relevant standards and empirical values of wood-based products. As for the wood-plastic composite material itself, since it has the characteristics of both wood and plastic, in the actual application of the product, how to use the material reasonably to meet the basic mechanical performance requirements of the product and avoid unsafe factors such as brittle failure of components, while also improving the utilization rate of raw materials and reducing costs. This has become a key issue to be addressed in future product design.
Bamboo Furniture
Bamboo is a specialty of Asia, distributed in southwest, central and south and east China. It grows much faster than trees and can be processed and used in only three to five years. Therefore, from the supply point of view, it can be said to be an "inexhaustible" natural resource. From ancient times to the present, bamboo furniture has been widely used in various regions south of the Yellow River in China. According to relevant historical records, China had bamboo furniture as early as the Tang and Song Dynasties. From some Buddhist portraits in the Tang and Song Dynasties, we can see bamboo furniture such as four-headed official hat chairs, footstools, and Zen chairs made of bamboo. However, due to the difficulty of long-term preservation, the actual bamboo furniture before the Qing Dynasty is no longer visible. Even the bamboo furniture left over from the Qing Dynasty is rare, but from the relevant historical research and analysis of its impact on hardwood furniture, Ming and Qing bamboo furniture was very popular. The existing bamboo furniture mainly includes traditional styles of stools, chairs, tables, Beds, cabinets, shelves, tables, desks, screens, etc.
With the development of science and technology, the connotation and extension of bamboo furniture have changed greatly. Bamboo can not only be directly used to process traditional round bamboo furniture, but also can be sawed into bamboo slices, peeled into bamboo veneers, sliced into bamboo thin slices, and made into bamboo plywood, bamboo laminates (laminated boards), bamboo integrated materials, bamboo particle boards, bamboo fiberboards and other bamboo artificial boards. Compared with bamboo, bamboo artificial boards have the following characteristics: large format, small deformation, stable size; high strength, good rigidity, wear resistance; certain insect and anti-corrosion properties; various coverings and coatings can be carried out to meet different use requirements. In addition, bamboo artificial boards can also be modified by mildew, mothproofing, carbonization, softening, bleaching, dyeing and other modification treatments.
Rattan Furniture
Rattan is abundant in tropical and subtropical jungles, growing and distributed in tropical areas such as Asia, Oceania, and Africa.Area. China has a long history of developing and utilizing rattan. Before the appearance of high-foot furniture, people used mats and couches for sitting and lying, including mats woven from rattan. Since the Han Dynasty, with the development of productivity and the improvement of the level of rattan making technology, the variety of Chinese furniture has increased day by day, and rattan chairs, rattan beds, rattan boxes, and rattan handicrafts have appeared one after another. Many famous museums in Europe and the United States still collect Chinese rattan furniture intact.
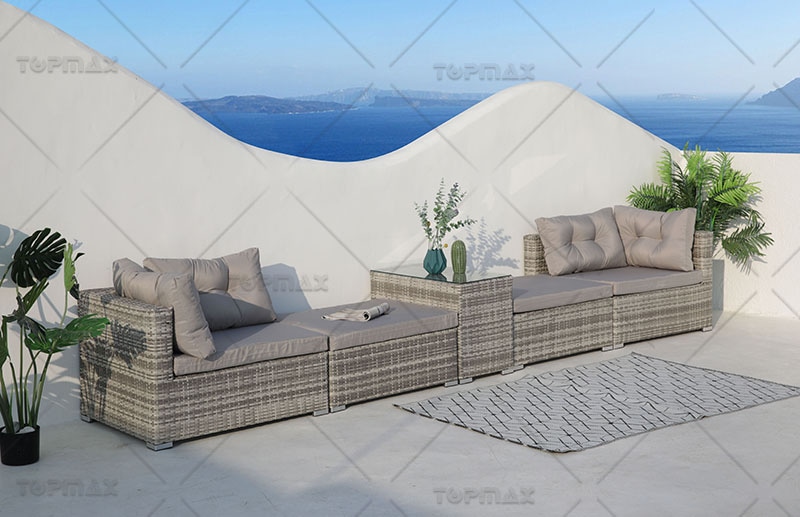
The natural texture, soft color, high strength, high toughness, easy processing, easy bending and deformation of rattan materials give rattan furniture simple and concise, fresh and elegant, free and casual, and dynamic style characteristics. Rattan furniture can be divided into four types according to the different parts of rattan materials used: rattan leather furniture, rattan core furniture, original rattan furniture, and polished rattan furniture.

Metal Furniture
In modern industrial society, metal materials are widely used for their excellent mechanical properties, processing properties and unique surface characteristics, especially in the furniture industry. The metal materials in furniture mainly include various pipes, plates and profiles made of cast iron and steel.
(1) Cast iron
Cast iron is a black metal with a carbon content of more than 2%. The material is heavy and brittle, has no ductility, high compressive strength, and has a rich texture effect on the surface. It is natural and simple, giving people a sense of heavy historical accumulation. It is often used in furniture bases, brackets and other supporting parts, or partial iron decorations on the facade of furniture, antique and European furniture design, etc., which not only carries a heavy history but also embodies the nostalgia of modern people.
(2) Steel
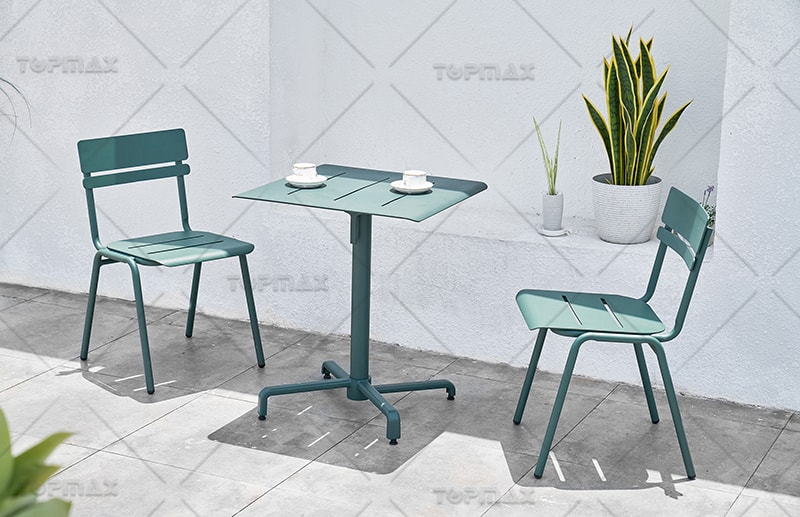
Steel is a material with a carbon content of 0.03%-0.2%, and its mechanical properties such as tensile strength, shear strength, elasticity, and toughness are very excellent. Steel structure furniture has a unique shape, is hard and upright, and has a sense of technology, modernity and strength, unifying artistry and practicality. The steel used in furniture making is mostly carbon steel, mainly in the form of steel plates and steel pipes. According to its shape, it can be divided into steel sections (round steel, flat steel and angle steel), steel pipes (welded steel pipes and seamless steel pipes), and steel plates (thin steel plates, which can be used as panel parts below 4mm). Metal furniture is usually assembled and shaped by welding, screws, pins and other connection methods. The structural forms are diverse, usually disassembly, folding, overlapping, plug-in, etc. For example, the metal and wood combined garden leisure tables and chairs shown in Figure 5-1-12, that is, steel-wood furniture, are made of metal pipes or plates as the main frame substrate of the furniture, and are combined and designed with natural wood materials that have been specially treated with anti-corrosion and anti-mildew in appropriate positions that are in direct contact with the human body, such as the backrest, seat, armrests and table tops. Compared with traditional wooden chairs, metal chairs are lighter, stronger and less prone to deformation. GLOSTER's KORE series of metal teak leisure tables and chairs use stainless steel metal pipes and profiles as the structural skeleton. The wooden surface substrate is fixed to the metal frame through plug-in, overlap, screws, bolts and other connection methods. It has a good load-bearing effect and high stability. This type of furniture not only overcomes the cold feeling of single metal furniture and the poor comfort caused by strong thermal conductivity, but also creates a contrast effect of rigidity and softness, artificiality and nature, cold and upright and gentle and heavy, modern and simple through the combination of metal and wood materials, enriching the visual effect and psychological feeling of metal furniture.

Glass Furniture
Glass is a transparent artificial material with good waterproof, acid and alkali resistance and moderate fire resistance and wear resistance. It can be processed by cutting, carving, sandblasting, chemical corrosion and other artistic treatments to obtain transparent or opaque effects to form pattern decoration and enrich the facade effect of furniture shape.
Glass is a commonly used material in furniture such as cabinet doors, shelves, coffee tables, and dining tables. The combination of wood, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, etc. with glass can greatly enhance the decorative value of furniture. In modern furnishings design, the design of furniture and lamps is increasingly moving towards combination. Due to its transparent characteristics, glass plays a decorative role of virtual and real intersection and mutual reflection under the background of furniture and lighting effects.
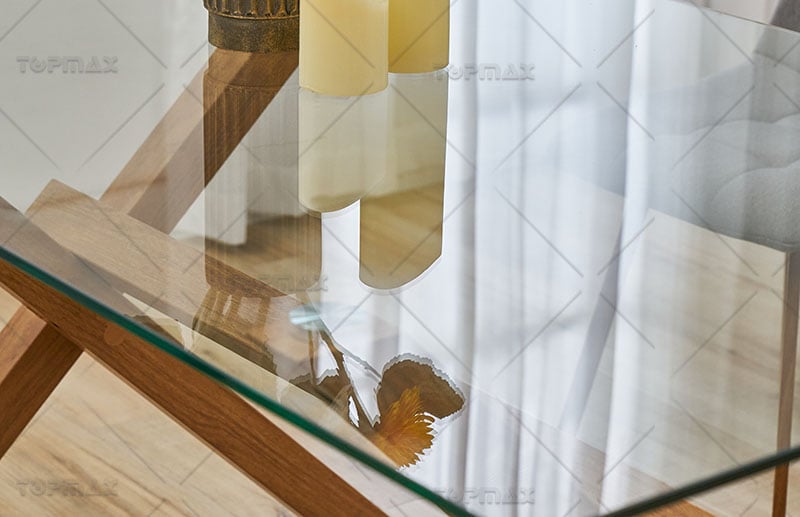

Greg Klassen, a furniture designer living in the coastal area of the northwest United States, designed a series of "River" tables. The wood he chose comes from recycled trees. He cut the collected logs along the grain, and then cut out blue-green glass representing the river along the edge, and inlaid it into the wood. The blue-green glass on the table looks like a winding river.
Commonly used glass in furniture manufacturing includes polished glass, tempered glass, curved glass, colored glass, mirrored glass, etc. Among them, tempered glass is often used as furniture tabletops, with thicknesses of 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, 15mm, etc., and curved tempered glass has three thicknesses of 5mm, 6mm, and 8mm.
Plastic Furniture
Plastic is an emerging and constantly improving artificial synthetic material. Since the 19th century, it has developed rapidly and has a wide range of uses. In the mid-1960s, the Italian design community advocated the development of plastic furniture. With rich colors and simple and varied shapes, it combines complex functions in simple forms, opening up new design paths for modern furniture.
Plastics can be processed into any shape people want through molding processes such as injection molding, blow molding, extrusion molding, compression molding, thermoforming, calendering, rotational molding, casting, and slush molding, which provides the possibility for the diversity of product form design. However, after being exposed to natural stresses such as sunlight, wind and rain for a long time, plastics will age, fade, crack, and lose strength. Therefore, they are rarely used alone in outdoor furniture and are often used in combination with materials such as metal and stone.

Commonly used plastic materials in furniture design include reinforced fiberglass plastic (FRP), styrene-butadiene-acrylonitrile terpolymer resin (ABS), acrylic resin (acrylic), polyurethane foam plastic (foamed plastic), polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), etc. For example, the "Miss Blanche" chair designed by Japanese designer Shiro Kuramata makes full use of the transparent material of acrylic resin, casting bright silk flowers in the transparent plexiglass chair shape, and the plate shape of plexiglass and aluminum alloy legs form a simple shape. The TwigPlastic product designed by Alexander Lotersztain is a modular and interactive luminous public seat that combines seating and lighting functions. It has a beautiful and stylish shape. The seat is mainly made of durable polyethylene material, and has a built-in LED light source. After power is turned on, it can provide 100-150 lux of illumination, adding a beautiful scene to the city night. Designer Davide G Aquini designed a series of Marbled Stools, which look like cool granite with beautiful patterns, but when people sit on them, they feel soft. The designer chose a soft polyurethane mixture to completely simulate granite and create a beautiful lie, hoping that everyone who sits down can feel the embrace and love of nature.
 Inquire Now
Inquire Now


 Home
Home Basic Dimensions and Design Requirements of Seats
Basic Dimensions and Design Requirements of Seats  You May Also Like
You May Also Like 





















 Tel
Tel  Email
Email  ADDRESS
ADDRESS 














